Why This Page?
I originally was going to write a page on CREATIONISM but then decided not to write in a negative fashion on actually a small niche that only fundamentalists latch onto but instead I should rather take the high road, stay scientific, and show what the majority of scientists worldwide believe and more importantly, why. To ignore mainstream science requires one to presuppose a particular belief system and then pick and choose science that supports your presupposed belief system. This methodology is not real science and is against the basic idea of scientific theory. Some fundamentalists do this, without even realizing it, because they fear that if any bit of their overall belief system is found not to be true, then perhaps their whole belief may collapse and be found to be false. In some cases it could result in a mental breakdown or a return to dangerous addictions or lifestyle that were left after adopting their religious belief system (whether Christian, Muslim, etc.) and the accompanying alienation from their family, spouse, church and/or school. Care should be exercised.
To summarize I have taken provided some paragraphs explaining the basic theory of evolution, human evolution, and radiometric dating with links so that people can go off and learn more if they wish. I have also included a criticism of Biblical fundamentalism from Wikipedia along with scientific critiques of Young Earth Creationism. -Shawn
Evolution Background From Britannica
"evolution, theory in biology postulating that the various types of plants, animals, and other living things on Earth have their origin in other preexisting types and that the distinguishable differences are due to modifications in successive generations. The theory of evolution is one of the fundamental keystones of modern biological theory."
"The virtually infinite variations on life are the fruit of the evolutionary process. All living creatures are related by descent from common ancestors. Humans and other mammals descend from shrewlike creatures that lived more than 150 million years ago; mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fishes share as ancestors aquatic worms that lived 600 million years ago; and all plants and animals derive from bacteria-like microorganisms that originated more than 3 billion years ago. Biological evolution is a process of descent with modification. Lineages of organisms change through generations; diversity arises because the lineages that descend from common ancestors diverge through time."
"Darwin and other 19th-century biologists found compelling evidence for biological evolution in the comparative study of living organisms, in their geographic distribution, and in the fossil remains of extinct organisms. Since Darwin’s time, the evidence from these sources has become considerably stronger and more comprehensive, while biological disciplines that emerged more recently—genetics, biochemistry, physiology, ecology, animal behaviour (ethology), and especially molecular biology—have supplied powerful additional evidence and detailed confirmation. The amount of information about evolutionary history stored in the DNA and proteins of living things is virtually unlimited; scientists can reconstruct any detail of the evolutionary history of life by investing sufficient time and laboratory resources."
"Comparative anatomy also reveals why most organismic structures are not perfect. Like the forelimbs of turtles, horses, humans, birds, and bats, an organism’s body parts are less than perfectly adapted because they are modified from an inherited structure rather than designed from completely “raw” materials for a specific purpose. The imperfection of structures is evidence for evolution and against antievolutionist arguments that invoke intelligent design (see below Intelligent design and its critics)."
"Embryonic rudiments that never fully develop, such as the gill slits in humans, are common in all sorts of animals. Some, however, like the tail rudiment in humans, persist as adult vestiges, reflecting evolutionary ancestry. The most familiar rudimentary organ in humans is the vermiform appendix. This wormlike structure attaches to a short section of intestine called the cecum, which is located at the point where the large and small intestines join. The human vermiform appendix is a functionless vestige of a fully developed organ present in other mammals, such as the rabbit and other herbivores, where a large cecum and appendix store vegetable cellulose to enable its digestion with the help of bacteria. Vestiges are instances of imperfections—like the imperfections seen in anatomical structures—that argue against creation by design but are fully understandable as a result of evolution."
"Darwin also saw a confirmation of evolution in the geographic distribution of plants and animals, and later knowledge has reinforced his observations. For example, there are about 1,500 known species of Drosophila vinegar flies in the world; nearly one-third of them live in Hawaii and nowhere else, although the total area of the archipelago is less than one-twentieth the area of California or Germany. Also in Hawaii are more than 1,000 species of snails and other land mollusks that exist nowhere else. This unusual diversity is easily explained by evolution. The islands of Hawaii are extremely isolated and have had few colonizers—i.e, animals and plants that arrived there from elsewhere and established populations. Those species that did colonize the islands found many unoccupied ecological niches, local environments suited to sustaining them and lacking predators that would prevent them from multiplying. In response, these species rapidly diversified; this process of diversifying in order to fill ecological niches is called adaptive radiation."
"The field of molecular biology provides the most detailed and convincing evidence available for biological evolution. In its unveiling of the nature of DNA and the workings of organisms at the level of enzymes and other protein molecules, it has shown that these molecules hold information about an organism’s ancestry. This has made it possible to reconstruct evolutionary events that were previously unknown and to confirm and adjust the view of events already known. The precision with which these events can be reconstructed is one reason the evidence from molecular biology is so compelling. Another reason is that molecular evolution has shown all living organisms, from bacteria to humans, to be related by descent from common ancestor"
"The evidence of evolution revealed by molecular biology goes even farther. The degree of similarity in the sequence of nucleotides or of amino acids can be precisely quantified. For example, in humans and chimpanzees, the protein molecule called cytochrome c, which serves a vital function in respiration within cells, consists of the same 104 amino acids in exactly the same order. It differs, however, from the cytochrome c of rhesus monkeys by 1 amino acid, from that of horses by 11 additional amino acids, and from that of tuna by 21 additional amino acids. The degree of similarity reflects the recency of common ancestry. Thus, the inferences from comparative anatomy and other disciplines concerning evolutionary history can be tested in molecular studies of DNA and proteins by examining their sequences of nucleotides and amino acids. (See below DNA and protein as informational macromolecules.)"
"The authority of this kind of test is overwhelming; each of the thousands of genes and thousands of proteins contained in an organism provides an independent test of that organism’s evolutionary history. Not all possible tests have been performed, but many hundreds have been done, and not one has given evidence contrary to evolution. There is probably no other notion in any field of science that has been as extensively tested and as thoroughly corroborated as the evolutionary origin of living organisms."
Human Evolution
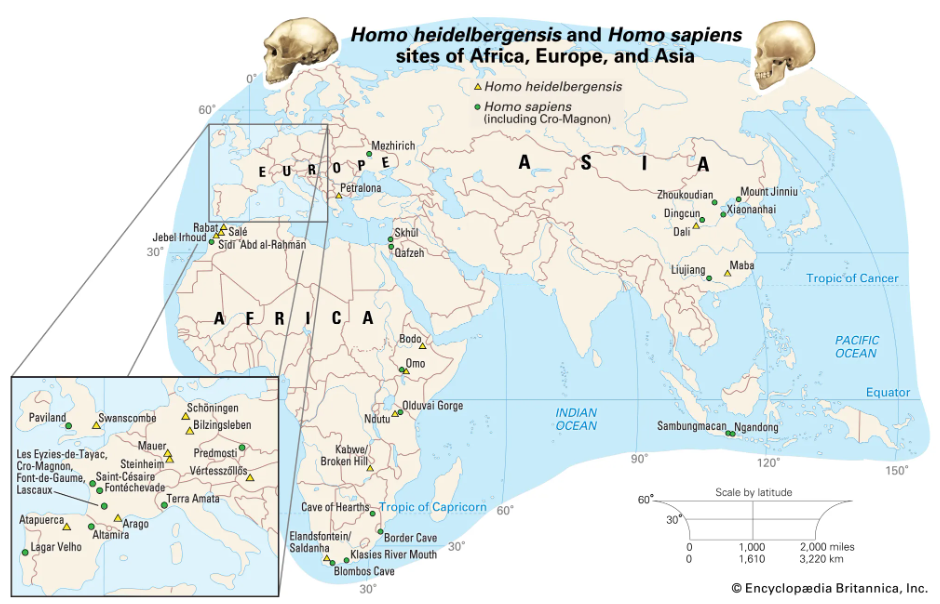
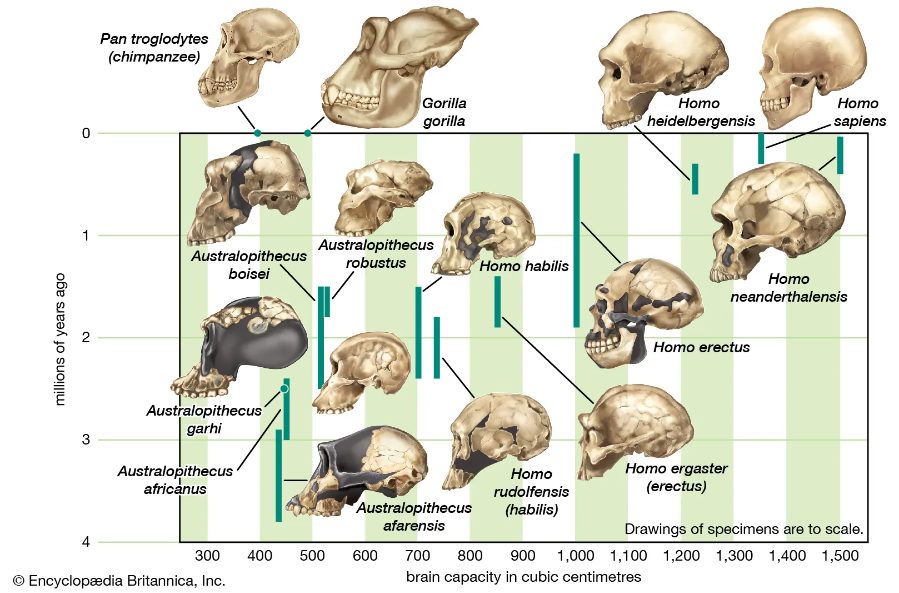
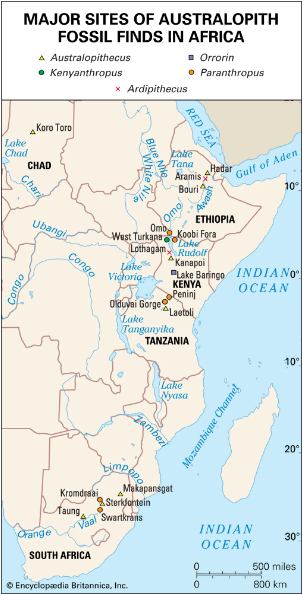
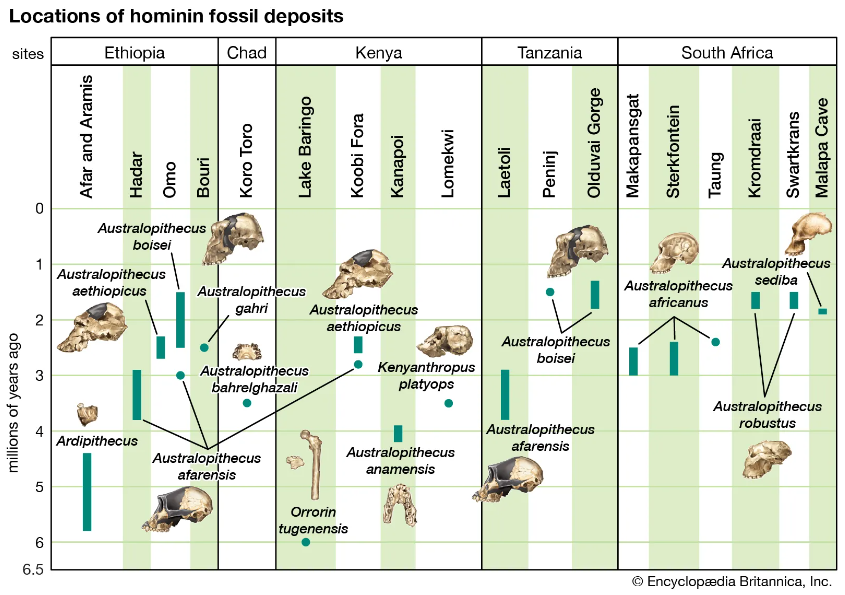
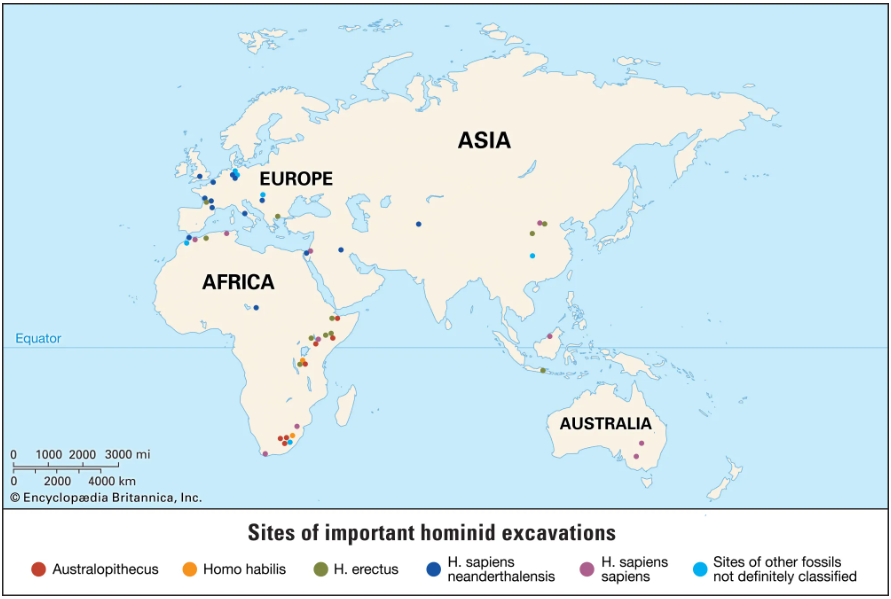
"The primary resource for detailing the path of human evolution will always be fossil specimens. Certainly, the trove of fossils from Africa and Eurasia indicates that, unlike today, more than one species of our family has lived at the same time for most of human history. The nature of specific fossil specimens and species can be accurately described, as can the location where they were found and the period of time when they lived; but questions of how species lived and why they might have either died out or evolved into other species can only be addressed by formulating scenarios, albeit scientifically informed ones. These scenarios are based on contextual information gleaned from localities where the fossils were collected. In devising such scenarios and filling in the human family bush, researchers must consult a large and diverse array of fossils, and they must also employ refined excavation methods and records, geochemical dating techniques, and data from other specialized fields such as genetics, ecology and paleoecology, and ethology (animal behaviour)—in short, all the tools of the multidisciplinary science of paleoanthropology."
"human evolution, the process by which human beings developed on Earth from now-extinct primates. Viewed zoologically, we humans are Homo sapiens, a culture-bearing upright-walking species that lives on the ground and very likely first evolved in Africa about 315,000 years ago. We are now the only living members of what many zoologists refer to as the human tribe, Hominini, but there is abundant fossil evidence to indicate that we were preceded for millions of years by other hominins, such as Ardipithecus, Australopithecus, and other species of Homo, and that our species also lived for a time contemporaneously with at least one other member of our genus, H. neanderthalensis (the Neanderthals). In addition, we and our predecessors have always shared Earth with other apelike primates, from the modern-day gorilla to the long-extinct Dryopithecus. That we and the extinct hominins are somehow related and that we and the apes, both living and extinct, are also somehow related is accepted by anthropologists and biologists everywhere."
"The emergence of the human nuclear family has been a particularly knotty problem for Western evolutionary theorists. Like bonobos and chimpanzees, people probably are fundamentally promiscuous, though such mating behaviour is heavily proscribed by the cultures into which individuals are born and reside. Indeed, theorists who wish to construct models of the emergence of hominin societies on the basis of extant ape societies seldom tackle the overriding fact that humans utilize a wide variety of kinship, social, sexual, and political arrangements, all of which are maintained and expressed symbolically as well as practically. Researchers often fail to search for the cognitive basis of symbolic representation, manipulation, and invention in apes, citing instead forms of behaviour that appear to harbinger specific human conditions. It will take the efforts of several scientific disciplines and sophisticated technology, probably over many years, to discover the underlying nature of our mental faculties, their neurological basis, and their development over time. Apes can play important roles in this enterprise only if they are allowed to survive in their natural habitats and only if they are viewed as being on their own evolutionary paths and not merely as steps toward the human condition."
"Yet the exact nature of our evolutionary relationships has been the subject of debate and investigation since the great British naturalist Charles Darwin published his monumental books On the Origin of Species (1859) and The Descent of Man (1871). Darwin never claimed, as some of his Victorian contemporaries insisted he had, that “man was descended from the apes,” and modern scientists would view such a statement as a useless simplification—just as they would dismiss any popular notions that a certain extinct species is the “missing link” between humans and the apes. There is theoretically, however, a common ancestor that existed millions of years ago. This ancestral species does not constitute a “missing link” along a lineage but rather a node for divergence into separate lineages. This ancient primate has not been identified and may never be known with certainty, because fossil relationships are unclear even within the human lineage, which is more recent. In fact, the human “family tree” may be better described as a “family bush,” within which it is impossible to connect a full chronological series of species, leading to Homo sapiens, that experts can agree upon"
Hominin Evolution Images
Radiometric Dating
"Together with stratigraphic principles, radiometric dating methods are used in geochronology to establish the geologic time scale. Among the best-known techniques are radiocarbon dating, potassium–argon dating and uranium–lead dating. By allowing the establishment of geological timescales, it provides a significant source of information about the ages of fossils and the deduced rates of evolutionary change. Radiometric dating is also used to date archaeological materials, including ancient artifacts."
"Radiometric dating, radioactive dating or radioisotope dating is a technique which is used to date materials such as rocks or carbon, in which trace radioactive impurities were selectively incorporated when they were formed. The method compares the abundance of a naturally occurring radioactive isotope within the material to the abundance of its decay products, which form at a known constant rate of decay. The use of radiometric dating was first published in 1907 by Bertram Boltwood and is now the principal source of information about the absolute age of rocks and other geological features, including the age of fossilized life forms or the age of Earth itself, and can also be used to date a wide range of natural and man-made materials."
"Different methods of radiometric dating vary in the timescale over which they are accurate and the materials to which they can be applied."
"All rocks and minerals contain long-lived radioactive elements that were incorporated into Earth when the Solar System formed. These radioactive elements constitute independent clocks that allow geologists to determine the age of the rocks in which they occur. The radioactive parent elements used to date rocks and minerals are:"
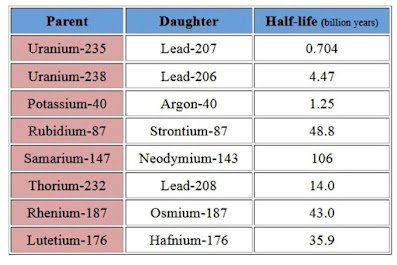
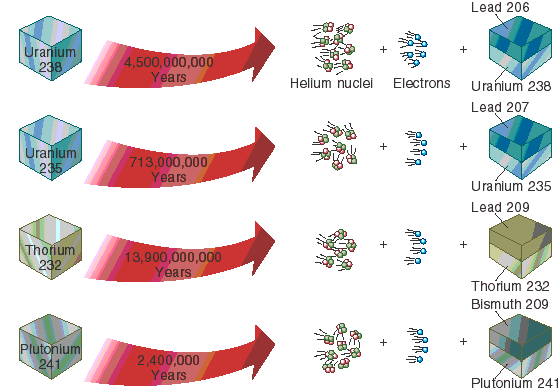
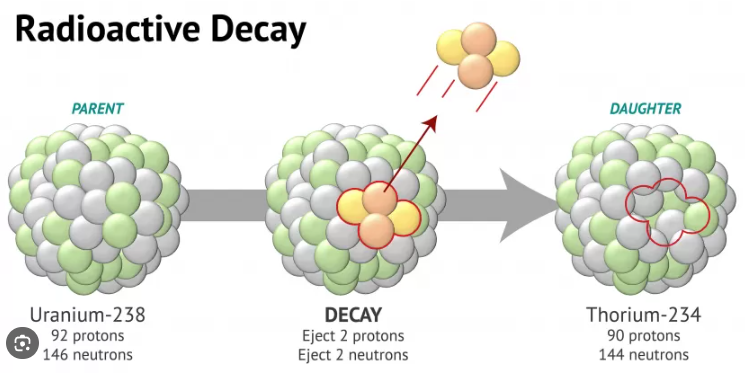
Absolute age: The numeric age of a layer of rocks or fossils. Absolute age can be determined using radiometric dating.
Era: The second largest division of time in the Geologic Time Scale, e.g., Mesozoic.
Eon: The largest division of time in the Geologic Time Scale, e.g., Phanerozoic.
Fauna: The animals of a given region or period.
Flora: The plants of a given region or period.
Fossil Record: All of the fossils that have existed throughout Earth’s history, whether they are in the ground or are in a museum.
Geologic Time Scale: A vertical timeline representing events in Earth’s history. The Geologic Time Scale is divided into blocks of time that represent great changes in Earth’s biodiversity.
Law of Superposition: The formation of new rock layers on top of older ones. This allows us to determine the relative age of rocks and fossils. "Super" refers to over and "position" refers to place.
Period: The third largest division of time in the Geologic Time Scale, e.g., Cretaceous.
Radiometric dating: A method used to determine the absolute age of a rock by using the rock's chemistry.
Relative age: The age of a rock layer, or the fossils it contains, compared to other layers.
Christian Fundamentalism Criticism
Fundamentalists' literal interpretation of the Bible has been criticized by practitioners of biblical criticism for failing to take into account the circumstances in which the Christian Bible was written. Critics claim that this "literal interpretation" is not in keeping with the message which the scripture intended to convey when it was written, and it also uses the Bible for political purposes by presenting God "more as a God of judgement and punishment than as a God of love and mercy."
Christian fundamentalism has also been linked to child abuse and mental illness as well as to corporal punishment, with most practitioners believing that the Bible requires them to spank their children. Artists have addressed the issues of Christian fundamentalism, with one providing a slogan "America's Premier Child Abuse Brand."
Fundamentalists have attempted and continue to attempt to teach intelligent design, a hypothesis with creationism as its base, in lieu of evolution in public schools. This has resulted in legal challenges such as the federal case of Kitzmiller v. Dover Area School District which resulted in the United States District Court for the Middle District of Pennsylvania ruling the teaching of intelligent design to be unconstitutional due to its religious roots.





 using WordPress and Kubio.
using WordPress and Kubio.