Do *YOU* Use Reason In Your Decisions?
From Wikipedia at https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Reason
“Reason is the capacity of applying logic consciously by drawing conclusions from new or existing information, with the aim of seeking the truth. It is closely associated with such characteristically human activities as philosophy, science, language, mathematics, and art, and is normally considered to be a distinguishing ability possessed by humans. Reason is sometimes referred to as rationality.”
“Reasoning is associated with the acts of thinking and cognition, and involves the use of one’s intellect. The field of logic studies the ways in which humans can use formal reasoning to produce logically valid arguments. Reasoning may be subdivided into forms of logical reasoning, such as deductive reasoning, inductive reasoning, and abductive reasoning. Aristotle drew a distinction between logical discursive reasoning (reason proper), and intuitive reasoning, in which the reasoning process through intuition—however valid—may tend toward the personal and the subjectively opaque. In some social and political settings logical and intuitive modes of reasoning may clash, while in other contexts intuition and formal reason are seen as complementary rather than adversarial. For example, in mathematics, intuition is often necessary for the creative processes involved with arriving at a formal proof, arguably the most difficult of formal reasoning tasks.”
“Reasoning, like habit or intuition, is one of the ways by which thinking moves from one idea to a related idea. For example, reasoning is the means by which rational individuals understand sensory information from their environments, or conceptualize abstract dichotomies such as cause and effect, truth and falsehood, or ideas regarding notions of good or evil. Reasoning, as a part of executive decision making, is also closely identified with the ability to self-consciously change, in terms of goals, beliefs, attitudes, traditions, and institutions, and therefore with the capacity for freedom and self-determination.”
What Is Cognitive Dissonance?
From ChatGPT:
“Cognitive dissonance refers to the psychological discomfort that arises when a person holds conflicting beliefs, values, or attitudes, or when their behavior contradicts their beliefs. It is a state of mental tension that occurs when there is an inconsistency between thoughts or between thoughts and actions. Resolving cognitive dissonance often involves adjusting beliefs or seeking information that aligns with one’s existing beliefs, in order to reduce the discomfort caused by the conflicting thoughts.”





Conspiracy Theories
From Wikipedia at https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Conspiracy_theory
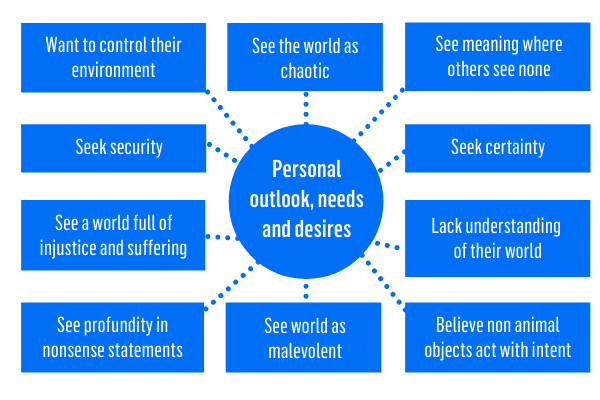
A conspiracy theory is an explanation for an event or situation that asserts the existence of a conspiracy by powerful and sinister groups, often political in motivation, when other explanations are more probable. The term generally has a negative connotation, implying that the appeal of a conspiracy theory is based in prejudice, emotional conviction, or insufficient evidence. A conspiracy theory is distinct from a conspiracy; it refers to a hypothesized conspiracy with specific characteristics, including but not limited to opposition to the mainstream consensus among those who are qualified to evaluate its accuracy, such as scientists or historians.
Conspiracy theories are generally designed to resist falsification and are reinforced by circular reasoning: both evidence against the conspiracy and absence of evidence for it are misinterpreted as evidence of its truth, whereby the conspiracy becomes a matter of faith rather than something that can be proven or disproven. Studies have linked belief in conspiracy theories to distrust of authority and political cynicism. Some researchers suggest that conspiracist ideation—belief in conspiracy theories—may be psychologically harmful or pathological, and that it is correlated with lower analytical thinking, low intelligence, psychological projection, paranoia, and Machiavellianism. Psychologists usually attribute belief in conspiracy theories to a number of psychopathological conditions such as paranoia, schizotypy, narcissism, and insecure attachment, or to a form of cognitive bias called “illusory pattern perception“. However, a 2020 review article found that most cognitive scientists view conspiracy theorizing as typically nonpathological, given that unfounded belief in conspiracy is common across cultures both historical and contemporary, and may arise from innate human tendencies towards gossip, group cohesion, and religion.
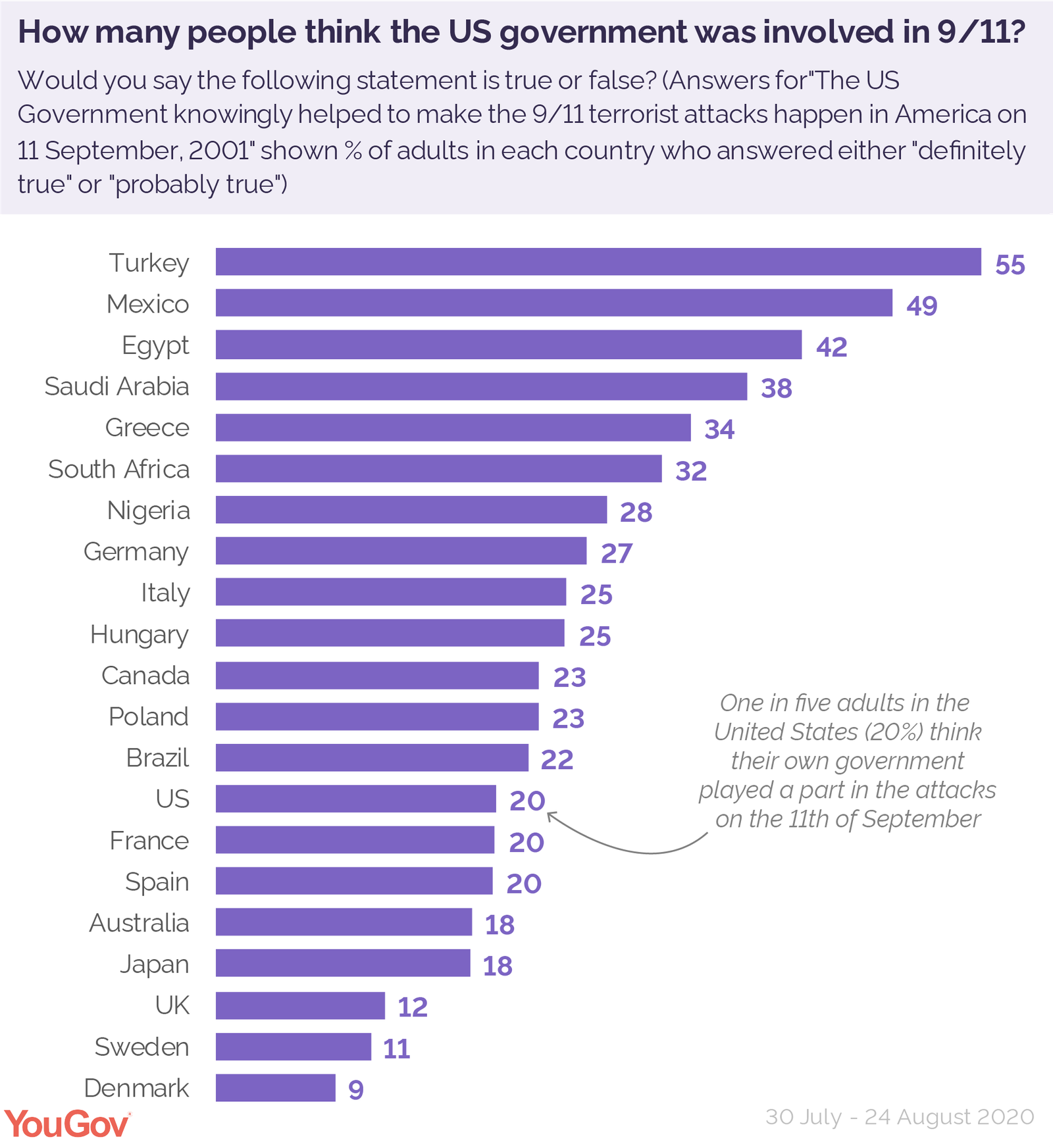
Historically, conspiracy theories have been closely linked to prejudice, propaganda, witch hunts, wars, and genocides. They are often strongly believed by the perpetrators of terrorist attacks, and were used as justification by Timothy McVeigh and Anders Breivik, as well as by governments such as Nazi Germany, the Soviet Union, and Turkey. AIDS denialism by the government of South Africa, motivated by conspiracy theories, caused an estimated 330,000 deaths from AIDS, QAnon and denialism about the 2020 United States presidential election results led to the January 6 United States Capitol attack, while belief in conspiracy theories about genetically modified foods led the government of Zambia to reject food aid during a famine, at a time when three million people in the country were suffering from hunger. Conspiracy theories are a significant obstacle to improvements in public health, encouraging opposition to vaccination and water fluoridation among others, and have been linked to outbreaks of vaccine-preventable diseases. Other effects of conspiracy theories include reduced trust in scientific evidence, radicalization and ideological reinforcement of extremist groups, and negative consequences for the economy.
Conspiracy theories once limited to fringe audiences have become commonplace in mass media, the internet, and social media, emerging as a cultural phenomenon of the late 20th and early 21st centuries. They are widespread around the world and are often commonly believed, some even being held by the majority of the population. Interventions to reduce the occurrence of conspiracy beliefs include maintaining an open society and improving the analytical thinking skills of the general public.








Statistics
Used by science to compare data sets and experimental data to arrive at conclusions and to help agree or disagree with existing studies, to refine theories, etc.
From ChatGPT:
“Statistics is a branch of mathematics that deals with the collection, analysis, interpretation, presentation, and organization of data. It involves methods for gathering data, summarizing it, and making inferences or predictions based on the observed patterns. Statistics plays a crucial role in various fields, including science, business, economics, social sciences, and more. By using statistical techniques, researchers and analysts can uncover patterns, relationships, and trends in data, enabling them to make informed decisions and draw meaningful conclusions.”
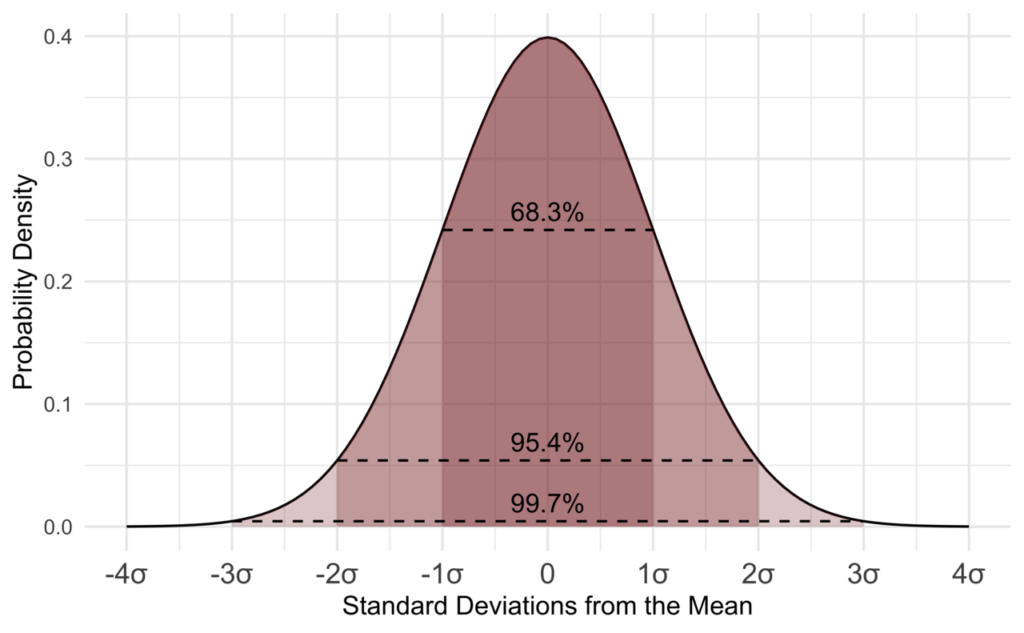
Standard Bell Curve :
The standard bell curve, also known as the normal distribution or Gaussian distribution, is a statistical concept used to describe the distribution of data in many natural phenomena. It is named after the mathematician Carl Friedrich Gauss.
The standard bell curve is characterized by a symmetrical, bell-shaped curve, with the highest point at the center and the data tapering off on both ends. In this distribution, most of the data points cluster around the mean or average value, with fewer points occurring further away from the mean.
The bell curve is often used to analyze and interpret data in various fields, including statistics, social sciences, and natural sciences. It helps in understanding patterns, making predictions, and determining probabilities. The curve’s properties, such as the mean and standard deviation, provide valuable insights into the data’s central tendency and variability.
Cartoons

 using WordPress and Kubio.
using WordPress and Kubio.